먼저 알아야 하는 것 : MST, Union-Find
Union-Find Algorithm
이걸 카테고리를 알고리즘으로 해야하는지... 자료구조로 해야하는지... * Union-Find (= disjoint-set / merge-find) 알고리즘 Union-Find 알고리즘은 2개의 기능을 가지고 있는 알고리즘이다. 1. Find : 어느 부..
superbono-2020.tistory.com
* Kruskal 정의
간선을 하나씩 선택해서 MST를 찾는 알고리즘. 그리디 알고리즘의 한 종류이다.
- 간선 리스트를 작성한다.
- 최초, 모든 간선을 가중치에 따라 오름차순으로 정렬한다.
- 가중치가 가장 낮은 간선부터 선택(두 정점을 해당 가중치의 비용으로 연결한다)하면서 트리를 증가시킨다. -> 사이클이 존재하면 다음으로 가중치가 낮은 간선 선택 (union-find를 사용하여 사이클의 존재 여부를 파악한다. 연결하려는 두 원소를 find 하여 대표자를 찾고, 대표자가 같지 않다면 union)
- n-1개의 간선이 선택될 때 까지 3번을 반복한다.
* Kruskal 적용 예
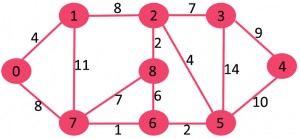
<간선 리스트>
가중치 출발 도착
1 7 6
2 8 2
2 6 5
4 0 1
4 2 5
6 8 6
7 2 3
7 7 8
8 0 7
8 1 2
9 3 4
10 5 4
11 1 7
14 3 5
<step 1>

가중치를 오름차순으로 정렬했을 때, 7과 6을 연결하는 1인 가중치가 가장 작으므로 연결한다.
<step 2>
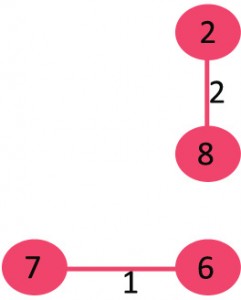
그 다음으로 작은 가중치(2)를 가지고 있는 2와 8을 연결하는 간선이 싸이클이 형성되지 않는지 확인한 후 간선을 연결한다.
<step 3>
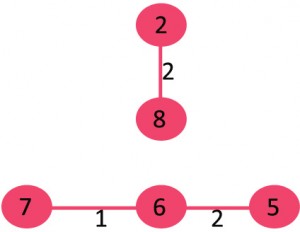
그 다음으로 작은 가중치(2)를 가지고 있는 6과 5을 연결하는 간선이 싸이클이 형성되지 않는지 확인한 후 간선을 연결한다.
<step 4>
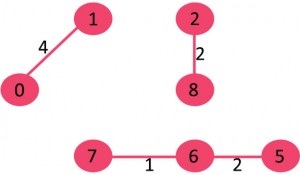
그 다음으로 작은 가중치(4)를 가지고 있는 1과 0을 연결하는 간선이 싸이클이 형성되지 않는지 확인한 후 간선을 연결한다.
<step 5>
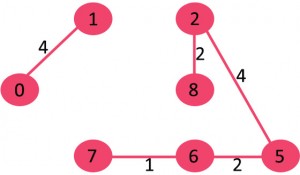
그 다음으로 작은 가중치(4)를 가지고 있는 2와 5를 연결하는 간선이 싸이클이 형성되지 않는지 확인한 후 간선을 연결한다.
<step 6>
그 다음으로 작은 가중치를 가지고 있는 간선은 8과 6을 6의 가중치로 연결하는 간선이지만, 해당 간선을 포함하면 싸이클이 형성되므로 버린다.
<step 7>
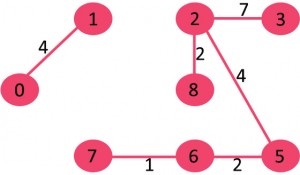
그 다음으로 작은 가중치(7)를 가지고 있는 2와 3을 연결하는 간선이 싸이클이 형성되지 않는지 확인한 후 간선을 연결한다.
<step 8>
그 다음으로 작은 가중치를 가지고 있는 간선은 8과 7을 7의 가중치로 연결하는 간선이지만, 해당 간선을 포함하면 싸이클이 형성되므로 버린다.
<step 9>
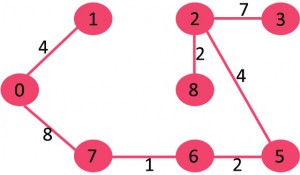
그 다음으로 작은 가중치(8)를 가지고 있는 0과 7을 연결하는 간선이 싸이클이 형성되지 않는지 확인한 후 간선을 연결한다.
<step 10>
그 다음으로 작은 가중치를 가지고 있는 간선은 1과 2를 8의 가중치로 연결하는 간선이지만, 해당 간선을 포함하면 싸이클이 형성되므로 버린다.
<step 11>
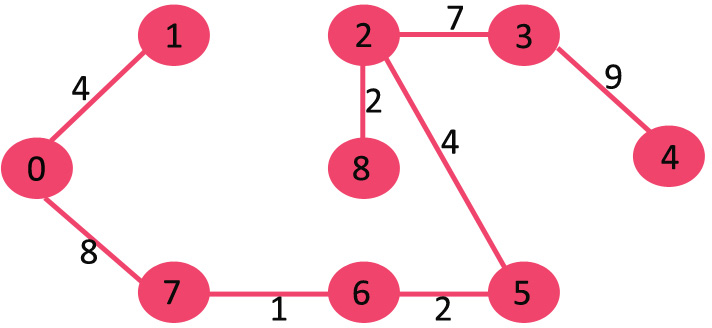
그 다음으로 작은 가중치(9)를 가지고 있는 3과 4를 연결하는 간선이 싸이클이 형성되지 않는지 확인한 후 간선을 연결한다. 9(n)개의 정점그래프에서 8(n-1)개의 간선을 선택하여 트리를 완성하였으므로 종료한다.
* Krulskal Algorithm Code for Java
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class Graph {
// 간선 그래프
class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>
{
int src, dest, weight;
// 간선 가중치를 오름차순으로 정리해줄 함수
public int compareTo(Edge compareEdge)
{
return this.weight - compareEdge.weight;
}
};
// union-find
class subset
{
int parent, rank;
};
int V, E; // V-> no. of vertices & E->no.of edges
Edge edge[]; // collection of all edges
// Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges
Graph(int v, int e)
{
V = v;
E = e;
edge = new Edge[E];
for (int i = 0; i < e; ++i)
edge[i] = new Edge();
}
// A utility function to find set of an
// element i (uses path compression technique)
int find(subset subsets[], int i)
{
// find root and make root as parent of i
// (path compression)
if (subsets[i].parent != i)
subsets[i].parent
= find(subsets, subsets[i].parent);
return subsets[i].parent;
}
// A function that does union of two sets
// of x and y (uses union by rank)
void Union(subset subsets[], int x, int y)
{
int xroot = find(subsets, x);
int yroot = find(subsets, y);
// Attach smaller rank tree under root
// of high rank tree (Union by Rank)
if (subsets[xroot].rank
< subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[xroot].parent = yroot;
else if (subsets[xroot].rank
> subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
// If ranks are same, then make one as
// root and increment its rank by one
else {
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
subsets[xroot].rank++;
}
}
// Kruskal
void KruskalMST()
{
// Tnis will store the resultant MST
Edge result[] = new Edge[V];
// An index variable, used for result[]
int e = 0;
// An index variable, used for sorted edges
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < V; ++i)
result[i] = new Edge();
// 간선 리스트를 오름차순으로 정렬
Arrays.sort(edge);
// Allocate memory for creating V ssubsets
subset subsets[] = new subset[V];
for (i = 0; i < V; ++i)
subsets[i] = new subset();
// Create V subsets with single elements
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
subsets[v].parent = v;
subsets[v].rank = 0;
}
i = 0; // Index used to pick next edge
// 정점(V) - 1 개의 간선을 선택할 때까지
while (e < V - 1)
{
// Step 2: Pick the smallest edge. And increment
// the index for next iteration
Edge next_edge = edge[i++];
int x = find(subsets, next_edge.src);
int y = find(subsets, next_edge.dest);
// If including this edge does't cause cycle,
// include it in result and increment the index
// of result for next edge
if (x != y) {
result[e++] = next_edge;
Union(subsets, x, y);
}
// Else discard the next_edge
}
// print the contents of result[] to display
// the built MST
System.out.println("Following are the edges in "
+ "the constructed MST");
int minimumCost = 0;
for (i = 0; i < e; ++i)
{
System.out.println(result[i].src + " -- "
+ result[i].dest
+ " == " + result[i].weight);
minimumCost += result[i].weight;
}
System.out.println("Minimum Cost Spanning Tree "
+ minimumCost);
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create following weighted graph
10
0--------1
| \ |
6| 5\ |15
| \ |
2--------3
4 */
int V = 4; // Number of vertices in graph
int E = 5; // Number of edges in graph
Graph graph = new Graph(V, E);
// add edge 0-1
graph.edge[0].src = 0;
graph.edge[0].dest = 1;
graph.edge[0].weight = 10;
// add edge 0-2
graph.edge[1].src = 0;
graph.edge[1].dest = 2;
graph.edge[1].weight = 6;
// add edge 0-3
graph.edge[2].src = 0;
graph.edge[2].dest = 3;
graph.edge[2].weight = 5;
// add edge 1-3
graph.edge[3].src = 1;
graph.edge[3].dest = 3;
graph.edge[3].weight = 15;
// add edge 2-3
graph.edge[4].src = 2;
graph.edge[4].dest = 3;
graph.edge[4].weight = 4;
// Function call
graph.KruskalMST();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija
출처 - https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/kruskals-minimum-spanning-tree-algorithm-greedy-algo-2/
Kruskal’s Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithm | Greedy Algo-2 - GeeksforGeeks
Minimum Spanning Tree for weighted, connected & undirected graph is a spanning tree with weight less than or equal to that of every other spanning tree.
www.geeksforgeeks.org
'CS > algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Binary Search Algorithm (이진 탐색 알고리즘) (0) | 2021.06.14 |
|---|---|
| PRIM MST Algorithm (프림 알고리즘) (0) | 2021.05.16 |
| MST(Minimum Spanning Tree): 최소 신장 트리 (0) | 2021.05.14 |
| 위상 정렬 (Topological Sorting) (0) | 2021.04.24 |
| Union-Find Algorithm (0) | 2021.04.14 |